工具管理 TOOL MANAGEMENT
- 绝对不要使用你在地上捡到的工具,或任何你不清楚其来历(它从哪来/接触过什么)的工具。这会让你面临以下风险:
- 破伤风 (tetanus)
- 血液疾病 (blood diseases)
- 艾滋病毒/艾滋病 (hiv/aids)
- 新冠肺炎 (covid 19)
- 以及其他潜在的危及生命的疾病
- 在使用 3-5 次后,或者如果有一段时间没用了,请把工具扔掉。
- 每次使用前后都要消毒,使用后的消毒尤其重要。用蘸过双氧水(hydrogen peroxide)的布擦拭最好,但用温水擦也行,只要之后彻底擦干就好。尽量别让工具用完后还带着血。
- 一定要检查有没有生锈,绝对不要用生锈的刀片,因为这有破伤风的风险。
- 把工具放在干燥的地方,远离潮湿和水。把它们收在干净的盒子、布或纸包装里。
- 扔工具的时候,把它们装在结实的药瓶里,或者用纸板和胶带裹好。随便乱扔利器可能会给环卫工人和处理垃圾的人带来危险。
- 带刀片出门要特别小心。偷偷把刀片带进住院部或精神病房可能被视为犯罪,并因此被起诉。很多学校也禁止带刀片入校,所以带着利器时要留意你所在的地方。
- NEVER use a tool you found on the ground or any tool you don't know the history from (where it came from/what it touched). this can put you at risk for
- tetanus
- blood diseases
- hiv/aids
- covid 19
- and other potentially life threatening diseases
- dispose of tools after 3-5 uses or if you haven't used it in a while
- disinfect before and after each use, this is especially important for after. wiping it off with a cloth soaked in hydrogen peroxide is ideal, but using warm water works just as well so long as it is thoroughly dried after. try not to leave your tools bloody after use.
- always check for rust, and never use a blade that has rust on it, as it puts you at risk for tetanus
- store your tools in a dry place away from humidity and water. keep them stored in a clean container, cloth, or paper package.
- when you throw out your tools, close them in a sturdy pill bottle or wrap them with cardboard and tape. disposing of sharps can be potentially dangerous for sanitation workers and anyone who ends up handling your trash.
- be very careful of where you take your blades. sneaking blades into an inpatient facility/psych ward can be considered a criminal offense and can be charged as one too. many schools also have policies against bringing blades on site, so be mindful of where you take sharps with you.
判断伤口深度 DETECTING THE DEPTH OF A WOUND
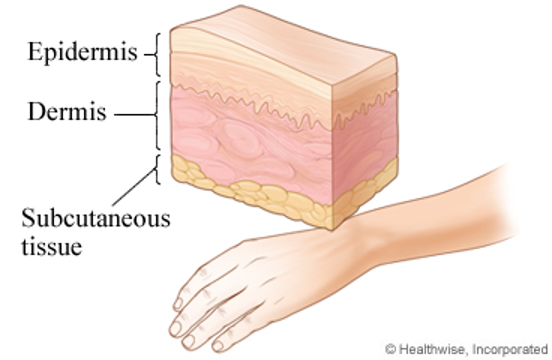
- 表皮 (Epidermis)(有时俗称“猫抓痕”):皮肤的最外层,伤口不会裂开。可能会出血,也可能不会,看有没有碰到毛细血管。
- 真皮 (Dermis)(有时俗称“styro”,指像泡沫塑料白色):伤到真皮层时,伤口会裂开,在血流出来之前能看到白色的皮肤层。一旦伤到这一层,就有碰到静脉、小动脉和神经的风险。感染风险也高得多。
- 皮下组织 (Hypodermis),也叫脂肪层(有时俗称“beans”,指像豆子一样的脂肪颗粒):这里有调节体温的血管网,当然还有脂肪。伤到这么深,伤口会裂得很大,露出黄色的细胞或脂肪“气泡”(这些气泡可能平的,也可能鼓出来)。脂肪层的伤口出血通常更快、时间更长,因为切到脂肪组织时会伤到毛细血管。在这一层,伤到大血管(如动脉和神经)的风险增加了。
- 筋膜 (Fascia):隔开皮下组织(脂肪)和肌肉的那一层。它看起来像在脂肪层下面的一层薄薄的白皮。伤到这更容易造成永久性损伤,上面提到的风险也都有。
- 肌肉 (Muscle):就在筋膜下面,呈红褐色。感染和瘫痪的几率增加,上面提到的风险也都有。
- epidermis (sometimes informally called “cat scratches” or “epis”) the first layer of skin, does not show a separation of skin. may or may not bleed, depending on whether you hit a capillary.
- dermis (sometimes informally called “styro”) - when you hit dermis, your wound will gape open and expose a white layer of skin before blood comes to fill in the wound. as soon as you hit styro, you put yourself at risk for hitting veins, arterioles, and nerves. risk of infection is a lot higher
- hypodermis, also known as the subcutaneous layer or the fat layer (sometimes informally called "beans") - contains both a network of blood vessels for thermoregulation and, of course, fat. cuts to this depth will gape wide open and expose yellow cells or “bubbles" of fat (these bubbles can appear flat or protrude outwards). fat cuts tend to bleed more rapidly and for longer because of the capillaries, which are a type of blood vessel, that are hit when you cut into fat tissue. the risk of hitting major blood vessels such as arteries and nerves increases at this layer.
- fascia - the layer that separates the subcutaneous tissue(fat) from muscle. it will appear as a thin white skin sitting underneath the fat layer. more likely to result in permanent damage, along with all the other risks mentioned above.
- muscle - the layer directly below the fascia, has a reddish brown color to it. increased chance of infection and paralysis, along with all the other risks mentioned above.
你伤到了什么? WHAT DID YOU HIT?
血管类型
- 毛细血管 (Capillary):最常见的血管。血的颜色不一样。不同类型的毛细血管出血速度和血量也不一样。在表皮或真皮层时,血流通常比较慢;但在皮下组织(脂肪)层,出血可能非常快。如果伤口出血了,但特征不像静脉、小动脉或动脉,那很可能就是毛细血管。
- 静脉 (Vein):血是暗红色或黑色的,像一股细细的、压力很高的水流一样流出来。(想象一下在塑料水瓶上扎个洞然后挤压它的样子)。
- 小动脉 (Arteriole):动脉的小分支。划伤或碰到时血会喷出来。血流会随着心跳一跳一跳的。血是鲜红色的,有时带点淡黄色。
- 动脉 (Artery):大量喷血,止不住。血流会随着心跳一跳一跳的。血是鲜红色的,有时带点淡黄色。
其他
- 神经 (Nerves):一旦碰到就会有像冲击波一样的疼痛:刺痛、针扎的感觉。也可能导致伤口区域麻木,或者肢体活动困难。轻微的神经损伤可以自己恢复,但严重的话,你可能会永久失去肢体的控制、感觉或功能。
types of blood vessels
- capillary - most common type of blood vessel. color of the blood varies. there are different types of capillaries which bleed at different speeds/produce different amounts of blood. when in the epidermis or dermis layers the flow of blood is often slow, whereas in the hypodermis(fat) layer the bleeding can be incredibly rapid. if your wound draws blood and the bleeding does not have the characteristics of a vein, arteriole, or artery, it is most likely a capillary.
- vein - flows in a thin, high pressure stream, dark red or blackish blood. (for visual reference, imagine poking a hole into a plastic water bottle and squeezing it)
- arteriole - a small branch of an artery. squirts when you nick or hit it. pulsates in time with your heart. bright red, sometimes yellowish blood
- artery - large amount of squirting blood that doesn’t stop. will pulsate in time with your heart. bright red, sometimes yellowish blood.
other
- nerves - shockwave of pain as soon as you hit it: stabbing pain, pins & needles sensation. can also lead to a numbness in the area of the wound/difficulty moving the limb. mild nerve damage can heal on its own, but in more severe scenarios you may permanently lose control/sensation/function of your limb
通用急救措施** GENERAL FIRST AID**
- 别用卫生纸、棉球、纸巾、餐巾纸或任何容易烂掉的东西擦伤口;碎屑掉进伤口会引起感染。
- 最好用干净的棉毛巾/布,如果没有,用不掉毛的纸巾也行。你也可以剪下不想穿的干净T恤用,只要它不掉毛。
- 如果伤口一直出血,用你的布/毛巾持续按压至少十分钟。意思是你要用最大的力气一直按着整整十分钟,中间别偷看。按压你看到血流出来的地方最有效。注意,如果你用来按压的东西容易烂掉,停止按压时它可能会粘在伤口上,把它扯下来会让血重新流出来,这步就白做了。这就是为什么用布/毛巾最好,你甚至可以在用之前在上面涂一层薄薄的抗菌药膏,防止粘连。如果可以,把受伤的部位抬高到心脏以上,能进一步减慢血流。
- 如果按压十分钟后还在出血,再按十分钟。如果之后还在流,强烈建议你去医院,特别是如果你觉得可能伤到了动脉或静脉(看“你伤到了什么”那部分)。用免缝胶带(steri strips)把伤口合上,或者在普通纱布上用加压绷带,是你自己处理的办法,但请只在绝对去不了医院的情况下才这么做。
- 尽量别抠痂!你抠痂就是揭掉了血凝块为了防止细菌进入伤口而筑起的盾牌,这是身体抵抗感染的自然防御。抠痂还可能让伤口重新裂开出血,阻碍愈合。
- 尽量用纱布/绷带/布条把伤口包起来。
- 每天换药,换药的时候要清洁伤口和周围区域。
- 在纱布上涂点抗菌药膏,防止它们粘在伤口上。如果伤口比真皮层深,不要直接把药膏涂在伤口里面。
- 处理伤口前,一定要用无香味的抗菌肥皂洗手。香精会刺激伤口,有时甚至导致感染。
- avoid using toilet paper, cotton balls, tissues, napkins, or anything else that breaks apart easily to clean your cuts; the debris can get into the wound, which can cause infection.
- using clean cotton towels/cloths is ideal, but if you don't have access to those you can use a paper towel that doesn't shed its fibers. you can also cut up a clean t-shirt you dont want and use that, so long as its fibers do not shed.
- if one of your cuts is continuously bleeding, use your cloth/towel and apply constant pressure for at least ten minutes. this means you press down on it as hard as you can for ten minutes straight, with no peeking in between. concentrating pressure on areas of the wound where you notice blood flowing is most effective. note that if what you are using to apply pressure breaks apart easily it may stick to your wound once you stop pressure, and pulling it off will only start the bleeding all over, negating this step entirely. this is another reason why using a cloth/towel is ideal, and you may even apply a very thin layer of some antibacterial ointment to it before using to further prevent sticking. if possible, raise the injured body part above the level of your heart to further slow blood flow.
- if the wound is still bleeding after ten minutes of successful, repeat the pressure again for the same duration. and if it's still bleeding after that, it is HIGHLY recommended that you seek hospital care, especially if you think the bleeding may be attributed to an artery or vein (see "what did you hit" section). closing your wound with steri strips and/or using compression bandages on top of regular wound dressings is a way you can mediate this yourself, but please only do this if you absolutely cannot seek medical attention.
- avoid picking your scabs as much as possible! when you do this, you are removing the shield your blood clots made to protect you from bacteria(etc) getting into your cut, which is the body's natural defense against infection. it can also reopen your wound to the point where it's bleeding, which sets you back in the process of healing.
- keep your wound covered with gauze/bandages/cloth wraps/etc as much as possible.
- change your coverings every day, and clean your wound/the area around it when you change them.
- apply antibacterial ointment to your dressings to prevent them from sticking to your wounds. don't apply ointment directly to your wounds if they breach deeper than dermis.
- before caring for wounds, it's important to wash your hands with antibacterial soap with no fragrance. fragrances can irritate your wounds and sometimes even lead to infection.
闭合愈合伤口 CLOSE HEALING A WOUND
- 强烈建议把任何裂开的伤口(真皮层或更深)合拢来愈合,这样疤痕更小,愈合快得多,感染风险也低。闭合愈合是目前最安全的伤口愈合方法。
- 闭合伤口需要免缝胶带(steri strips)。没有的话,可以用普通创可贴或医用胶带。实在不行,管道胶带(duct tape)也能凑合用。
- 先止血,用蒸馏水/盐水/抗菌溶液清洁伤口周围。然后用干净、干燥、不掉毛的毛巾/布拍干。
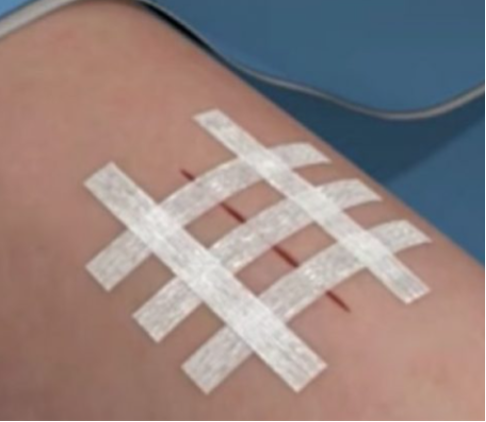
- 最好一条一条地贴免缝胶带,这样最准。贴的方向要和伤口垂直(看图一)。
- 把免缝胶带的一头粘在伤口旁边,按紧。然后用胶带把伤口拉拢,同时用另一只手从对面推一下。如果只用一只手,就只能靠胶带拉,这有点难。
- 伤口合拢后,把胶带拉过去粘好,保持拉紧的状态。记住,免缝胶带是为了拉住伤口,所以得贴紧。按压胶带确保粘牢了。
- 重复这个步骤,直到整个伤口都封住。通常从伤口一头贴到另一头。胶带之间的距离要均匀。
- 你可以顺着伤口方向再贴两条胶带加固一下(看图二)。
- 这里有个视频(原文链接),需要看演示的点这里。
- 伤口形成后24小时内都可以闭合。贴好后,让它保持7-9天左右。这期间尽量别碰水,尤其别搓洗那个地方。用大创可贴或纱布把整块盖住会有所帮助,但不是必须的。
- 如果伤口裂开超过0.5厘米(0.2英寸),强烈建议去缝针。话虽这么说,你绝对不能自己在家缝针,所以如果实在看不了医生,用免缝胶带闭合是退而求其次的办法。
- it's highly advised that any wounds that gape open (dermis or deeper) are healed closed, as it reduces scarring, decreases healing time tremendously, and decreases risk of infection. closed healing is by far the safest method of healing wounds.
- for closed healing, you need steri strips. if you don't have steri strips, you can use regular bandaids or medical/surgical tape. if you don't have either of those, you can use duct tape as a last resort.
- stop the bleeding and clean the area around the wound with distilled water/saline/antiseptic solution. then, pat it dry with a clean, dry towel/cloth that doesn't shed its fibers.
- it's best to apply steri strips one by one for the most precision. they are placed along wounds perpendicular to the actual incision (see image one).
- stick the first part of your steri strip right beside your wound, then press it down so it stays. after that, pull the wound shut from one side with the steri strip, and push it from the other side with your free hand. if you are only using one hand, you'll have to pull it closed using just the tape itself, which can be tricky.
- once your wound is closed, bring the tape over and stick it down, keeping the tension. remember, the purpose of steri strips are to hold wounds closed, so they need to be kept on tight. press down over the steri strip to ensure that it is stuck
- repeat until the entire wound is closed. usually, people start at one end of the wound and then go to the other. keep your steri strips evenly spaced
- you can add two additional steri strips parallel to your wound for extra security (see image two)
- here's a video for those who need a visual reference
- you can close a wound up for up to 24 hours after making it, and once you put them on you keep them on for around 7-9 days. try to avoid contact with water in that time, and especially avoid scrubbing the area. covering the entire area with a large bandaid or pad of gauze can be helpful, but is not necessary.
- it is highly recommended to get stitches for wounds that gape more than 0.5 centimeters(0.2 inches). that being said, you must NEVER stitch yourself at home, so if medical care simply isn't an option for you, the next best thing would be to steri strip your wounds.
表皮伤口护理 CARING FOR EPIDERMIS CUTS
止血后,用蒸馏水/盐水/抗菌溶液洗掉干血,贴上创可贴。如果你容易感染,也可以涂点抗生素药膏或无味凡士林,这也能止痒。这种伤口几天到一周就能好。
after you have stopped the bleeding, clean off all the dry blood with distilled water/saline/antiseptic solution and apply a bandage. you can also apply antibiotic ointment or unscented petroleum jelly/vaseline if you are prone to infection, which can also help with any itchiness that you experience. healing takes anywhere from a few days to a week.
真皮伤口护理 CARING FOR DERMIS CUTS
止血后,用蒸馏水/盐水洗掉血迹,然后涂抗菌溶液消毒。如果你不打算把伤口合拢(闭合愈合),就用纱布垫或不粘垫盖住,用医用胶带固定。在外面缠个加压绷带减少出血也是个好主意,但不是非做不可。你也可以在垫子上涂薄薄一层抗菌霜/药膏,防止它粘在伤口上。
每24-48小时换一次药,或者脏了、被血湿透了就换。每次换药都要清洁伤口。这种伤口敞开愈合可能需要一周到一个月。如果你想闭合愈合,请看上面的“闭合愈合伤口”部分。
after you have stopped the bleeding, clean off all the blood with distilled water/saline and then disinfect by applying antiseptic solution. if you are choosing not to closed heal, use gauze pads or a non stick pad and secure it with surgical/medical tape onto your wound. rolling a compression bandage on top to reduce blood flow is also a good idea, but isn't necessary. you can also apply a thin layer of antibacterial cream/ointment to the pad so it doesn't stick to your wound.
change bandages every 24-48 hours or if they get dirty/soaked through with blood. clean your wound each time you change them. these cuts can take one week to a month to open heal. if you're choosing to closed heal, please read the “close healing a wound” section above.
脂肪层或更深伤口护理 CARING FOR FAT CUTS OR DEEPER
脂肪层的伤口通常应该找专业医生处理,他们可以缝合伤口并更好地监控感染。如果你伤到了脂肪层或更深,请考虑就医。如果去不了医院,止血后可以参考以下做法。
- 抗菌溶液会损伤皮下组织,所以如果伤口深过真皮层,就只用蒸馏水/盐水冲洗。
- 记住,闭合脂肪层伤口是最安全的愈合方式,也能大大缩短愈合时间。如果你想闭合愈合,请看上面的“闭合愈合伤口”部分。
- 如果你不打算闭合愈合,在伤口边缘涂点抗菌霜,上面盖个纱布垫/不粘垫,用医用胶带固定。外面缠个加压绷带减少出血也是个好主意,但不是必须的。你也可以在垫子上涂薄薄一层抗菌霜/药膏,防止粘连。
- 每24-48小时换一次药,或者脏了、被血湿透了就换。每次换药都要清洁伤口。这种伤口敞开愈合可能需要几周到几个月。对于脂肪层伤口,了解正常愈合和感染的区别特别重要,因为它们愈合时会渗出淡黄色透明液体,看着挺恶心,但这其实是正常的,不是感染。
下面列出了你可能会遇到的症状和感染迹象,供参考。
fat cuts normally should be taken care of by a medical professional, who can stitch the wounds closed and better monitor for infection. if you cut to fat or deeper, please consider seeking medical attention. if that isn't an option, here are some tips on what to do after you have stopped the bleeding.
- antiseptic solutions actually damage subcutaneous tissue, so if your cut goes deeper than dermis, stick to distilled water/saline to wash it out.
- keep in mind that closing fat cuts is the safest way to heal them, and it also reduces the healing time dramatically. if you wish to closed heal your cut, please read the “close healing a wound” section above.
- if you are choosing not to closed heal, apply antibacterial cream around the edges of the wound and secure a gauze pad/non stick pad on top with medical tape. rolling a compression bandage on top to reduce blood flow is also a good idea, but isn't necessary. you can also apply a thin layer antibacterial cream/ointment to the pad so it doesn't stick to your wound.
- change bandages every 24-48 hours or if they get dirty/soaked through with blood. clean your wound each time you change them. these cuts can take anywhere from a couple weeks to a couple months to open heal. it's especially important to learn the difference between what normal healing looks like and the signs of an infection for fat cuts, as it's normal for them to leak out a yellowish-clear fluid as they heal and to look pretty disgusting despite not being infected.
symptoms you may experience and signs of infection are below for reference.
可能出现的症状** SYMPTOMS YOU MAY EXPERIENCE**
遇到这些情况完全正常,根本不是感染的迹象,特别是如果你没有出现下面列出的任何感染症状。
- 伤口周围有瘀青或按着疼:切割时,伤口周围皮肤下的小血管可能会破裂,导致瘀青和压痛。下手越快、越重,这种情况可能越严重。缝针周围也可能有瘀青。瘀青可以是各种深浅的紫色、红色、蓝色和黄色。
- 痒:身体愈合伤口、清除感染的过程通常会伴随着瘙痒。冷敷或用冰袋冰一下可以止痒。如果伤口只在表皮层没更深,也可以涂抗生素药膏或无味凡士林止痒。
- 组织液 (Serous fluid):身体为了帮助伤口愈合产生的一种水状、透明的淡黄/绿/棕色液体。伤口经常会渗出这种液体,通常伤口越深渗得越多。这可能会让你揭开绷带时看到上面有黄/绿色。组织液(正常)和脓(感染)最大的区别是,脓是不透明的,比较稠;而组织液很稀,像水一样。另外,有脓通常还会有其他感染迹象,所以如果你没看到其他感染迹象,伤口渗出的液体就不太可能是感染引起的。
- 对于更深的伤口:你可能会在伤口里看到白色/浅绿色的斑点(有时俗称“发霉”)。这是一种伤口渗出物,本质上是一团白细胞,它们在那里是为了促进愈合。
all of these are completely normal to experience and not at all an indicator for an infection, especially if you do not experience any of the infection signs listed in the section below.
- bruising or tenderness around wounds: when you cut, small blood vessels under the skin around the area of the cut may be broken, which causes bruising and tenderness. this effect can be exacerbated with increased speed and/or pressure in the act of cutting. this bruising can also be present around stitches. bruises can take on various shades of purple, red, blue, and yellow.
- itchiness: the body's natural process of healing a wound and clearing out infection often go hand in hand with an itching sensation. using a cold compress or an ice pack can alleviate this itch. if your wounds go to epidermis and no deeper you can also use antibiotic ointment or unscented petroleum jelly/vaseline to alleviate itching.
- serous fluid: a watery, clearish yellow/green/brown fluid that the body produces to help heal a wound. wounds can often leak this fluid, and often times the deeper they get the more fluid they will leak. this may create a yellow/green tint to your bandages that you see after you remove them. the big difference between serous fluid (normal) and pus (infection) is that pus is opaque and has a thicker consistency, whereas serous fluid is a lot more thin and watery. additionally, pus usually comes along with other signs of an infection, so if you are not seeing any other signs of infection it's not likely that the fluid leaking from your wound is related to infection.
- for deeper cuts: you may find white/light green spots in your wounds (sometimes informally called a "moldy” appearance). this is a type of wound exudate that is essentially a clump of white blood cells, which are there to facilitate healing.
过度肉芽化 OVERGRANULATION
过度肉芽化(也叫 hypergranulation)是深伤口可能出现的一种并发症,原因是愈合过程中伤口太湿了。比如绷带连续捂了超过24小时没换,就可能发生。过度肉芽化的伤口会从伤口里凸出来向外长(看下图),颜色是粉色或红色,质地有点像颗粒或小疙瘩。它们非常湿润、敏感,容易出血。在治好过度肉芽化之前,伤口可能很难愈合。
overgranulation(also called hypergranulation) is a complication that can occur in deeper wounds if it is too moist during healing, which can happen if bandages are continuously left on for more than 24 hours instead of being changed out. an overgranulated wound will bulge out of the wound bed and continue to grow outwards(see image below), with a pink or red color and somewhat grainy or sometimes lumpy texture. they are also very moist and sensitive/prone to bleeding. wounds that are overgranulated may have trouble healing until the overgranulation is treated.

医生可以开专门的绷带来治疗,所以如果能看医生,现在就去。否则,你可以在家治疗:用碘伏敷料(正常包扎,但在敷料和伤口之间加一块碘伏垫),或者涂氢化可的松乳膏(每8-12小时涂一次)。你也可以减少包扎时间,或者干脆敞开愈合(干燥愈合),但一定要定期清洁伤口。治疗过度肉芽化很慢,所以勤换绷带非常重要。注意,除非伤口过度肉芽化,否则不要用氢化可的松乳膏。
来源: "Using Topical Hydrocortisone 1% Cream" - NHS (guide for use), Evidence of Hydrocortisone Effectiveness
medical professionals can prescribe specific bandages for treatment, so if seeing a professional is an option for you this is the time to do so. otherwise, you can treat at home by implementing iodine wound dressings (dressing normally but with iodine pads in between the dressing and the cut) or hydrocortisone cream (applied to the wound every 8-12 hours) into your healing routine. you can also leave your coverings on for less time or completely switch to dry/uncovered healing, but be sure to keep cleaning your wound regularly. treating overgranulation is a very slow process, which is why it's important to be diligent about changing your bandages regularly. note that hydrocortisone cream should not be used on wounds unless they are overgranulated.
sources: "Using Topical Hydrocortisone 1% Cream" - NHS (guide for use), Evidence of Hydrocortisone Effectiveness
感染迹象** SIGNS OF AN INFECTION**
- 伤口摸起来比平时热
- 伤口周围红肿范围扩大
- 伤口比预期或平时更疼、更敏感
- 伤口周围肿胀、一按就疼
- 流出不透明的黄色或绿色脓液,通常有臭味(这是感染晚期的迹象)
- 发烧,这说明感染扩散了
如果你怀疑伤口感染了,可以用蒸馏水清洗;如果是真皮层或更浅的伤口,可以涂抗菌溶液。如果你只有上面提到的几个症状,伤口不一定感染了,可能只是受刺激了。常规清洁可以防止刺激变成感染。
- your wound feels hotter to the touch than normal skin
- there is an expanding redness around the wound
- the wound is more painful or sensitive than expected/usual
- there is swelling/tenderness/pain around the wound
- there is opaque yellow or green pus leaking, usually with an odor (this is a sign of a late-stage infection)
- a fever, which indicates that the infection is spreading
if you suspect that your wound is infected, you can clean it out with distilled water and, if dermis or shallower, apply antiseptic solution. if you are exhibiting only a few of the symptoms above, your wound may not necessarily be infected, only irritated. routine cleaning can prevent irritation from progressing to infection.
物资词汇表(含图) SUPPLY GLOSSARY (WITH IMAGES)

创可贴 (Bandaids)
通常有不同大小。像下图这种织物(布)创可贴质量好得多,如果能选就选这种。
纱布垫 (Gauze pads)
没有粘性,必须用医用胶带固定。可以用卫生巾代替,但记住它们不一定是无菌的。
bandaids
can usually be found in different sizes. fabric bandaids such as the one below are much higher quality, so if you have to pick choose those.
gauze pads
doesn't have any sticky parts, must be secured via medical tape. an alternative to these is to use menstrual pads, but keep in mind they aren't necessarily sterile.

免缝胶带 (Steri strips)
用于在伤口愈合时把伤口拉住,对真皮层或更深、裂开的伤口最理想。替代品有医用胶带甚至管道胶带。你也可以用蝴蝶绷带(butterfly bandages),它也可以用普通绷带、医用胶带或管道胶带自己做。我没多写蝴蝶绷带是因为我个人不喜欢用,如果你好奇,这里有个视频指南(原文链接)。
steri strips
used to hold wounds closed as they heal, which is ideal for wounds that reach dermis or deeper and/or gape open. alternatives include medical tape or even duct tape. you can also use butterfly bandages, which can also be fashioned from regular bandages, medical tape, or duct tape. i didn't include much on butterfly bandages because personally i don't like using them, but if you're curious here is a video guide.

蒸馏水 (Distilled water)
不含纯净水里可能有的矿物质的水(纯净水对伤口来说不一定无菌)。把自来水煮沸放凉也可以用,煮沸能去除杂质和矿物质。
抗菌溶液 (Antiseptic solution)
也叫“双氧水”(hydrogen peroxide),有喷雾瓶装的。
抗菌/抗生素软膏 (Antibacterial/antibiotic ointment)
也叫“外用抗生素”。美国品牌有 neosporin, aquaphor, bacitracin, polysporin 等。
生理盐水 (Saline)
通常叫“伤口清洗液”,有喷雾装。自己配的话,用4杯蒸馏水加2茶匙盐,搅拌溶解。(可以配不同量的盐水,但这比例不能变)。
distilled water
this is water that doesn't include any minerals that may be in purified water that may not be sterile for wounds. if you boil tap water and let it cool, you can use that as well, as boiling removes impurities and minerals.
antiseptic solution
can also be called "hydrogen peroxide”, and can come in spray bottles as well
antibacterial/antibiotic ointment
can also be called “topical antibiotic". brands in the us include neosporin, aquaphor, bacitracin, polysporin, etc.
saline
usually called “wound wash” and sold as a spray. made by combining four cups of distilled water and two teaspoons of salt, mixing until dissolved. (different amounts of saline can be made, but the ratio must remain the same)